Products: Abaqus/Standard Abaqus/Explicit Abaqus/CAE
Benefits: Abaqus/Standard and Abaqus/Explicit now allow for point masses to be anisotropic. This enhancement is useful when you are modeling submerged structures where the influence of the surrounding fluid is captured using “added mass” attached to the nodes of the structure. This modeling approximation often results in an added mass that is direction dependent.
Description: You can now define an anisotropic point mass element by specifying the three principal values and the principal directions. In a large-displacement analysis the local axes of the anisotropic mass rotate with the rotation, if active, of the node to which the anisotropic mass is attached. The rotation degree of freedom is active at a node if that node is connected to a beam, a conventional shell, a rotary inertia element, or a rigid body. You can also specify mass proportional alpha damping and loads such as gravity for the anisotropic point mass.
Property or Interaction module:
Special Inertia
Inertia Create: Point mass/inertia: select point: Magnitude: Anisotropic:
Create: Point mass/inertia: select point: Magnitude: Anisotropic:
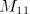 ,
, 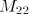 , and
, and